
The dream of many people is to create an app from scratch. Perhaps because they saw the movie The Social Network and want to be Mark Zuckerberg. Or because they really have a clear idea and want to create an app for their business.
Whatever your motivation, I want to show you where to start and what knowledge you need to create a mobile application. In this guide, we will study the steps of the best mobile development teams and how you can follow them to create your own professional mobile application.
So, what is needed to create an app from scratch?
- Design the mobile application
- Choose the tools to program the app
- Develop the mobile app (choose the code)
Let's look at these 3 steps in more detail to create a mobile application.
Learn: What are web applications? Features and examples.
1. Start with mobile app design
1.1. Diagram the Mockups
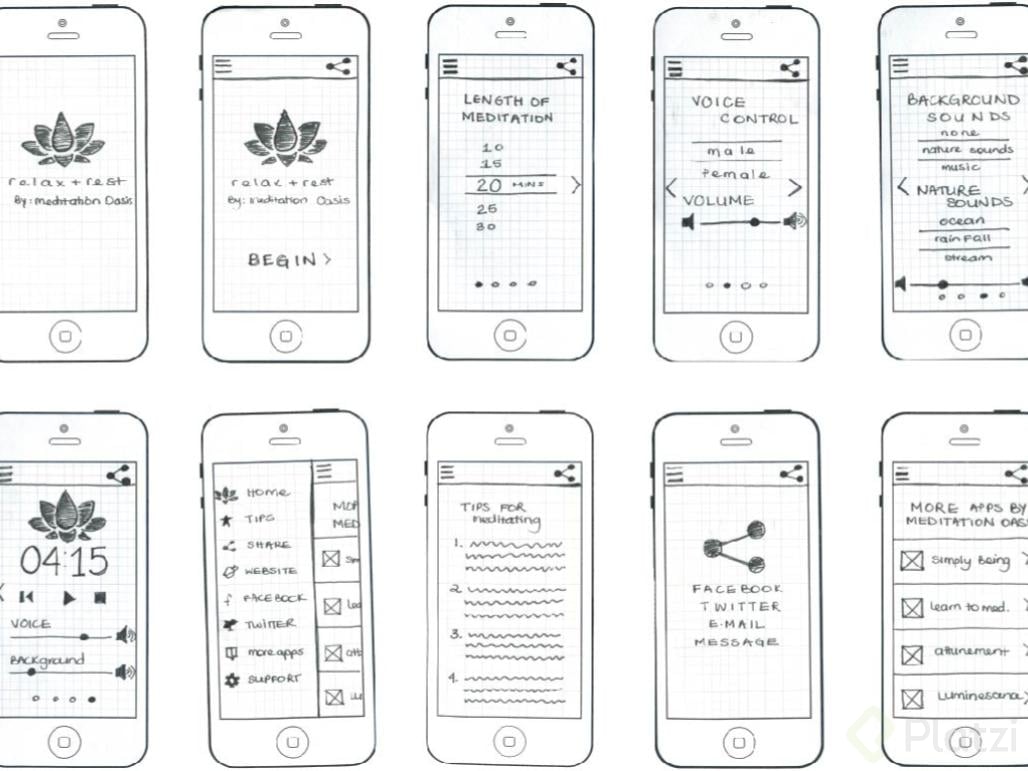
The first step to creating a mobile app is not programming. It's creating a mockup. A very low-resolution version to test your idea. You can use pencil and paper. Although there are also excellent digital tools such as Balsamiq Mockups or InVision Freehand.
1.2. Have your UI Kit ready
An UI Kit is all the screens of our application and how they are connected. We also know it as a Storyboard. Want to learn more about designing a mobile app? Let's start with the following:
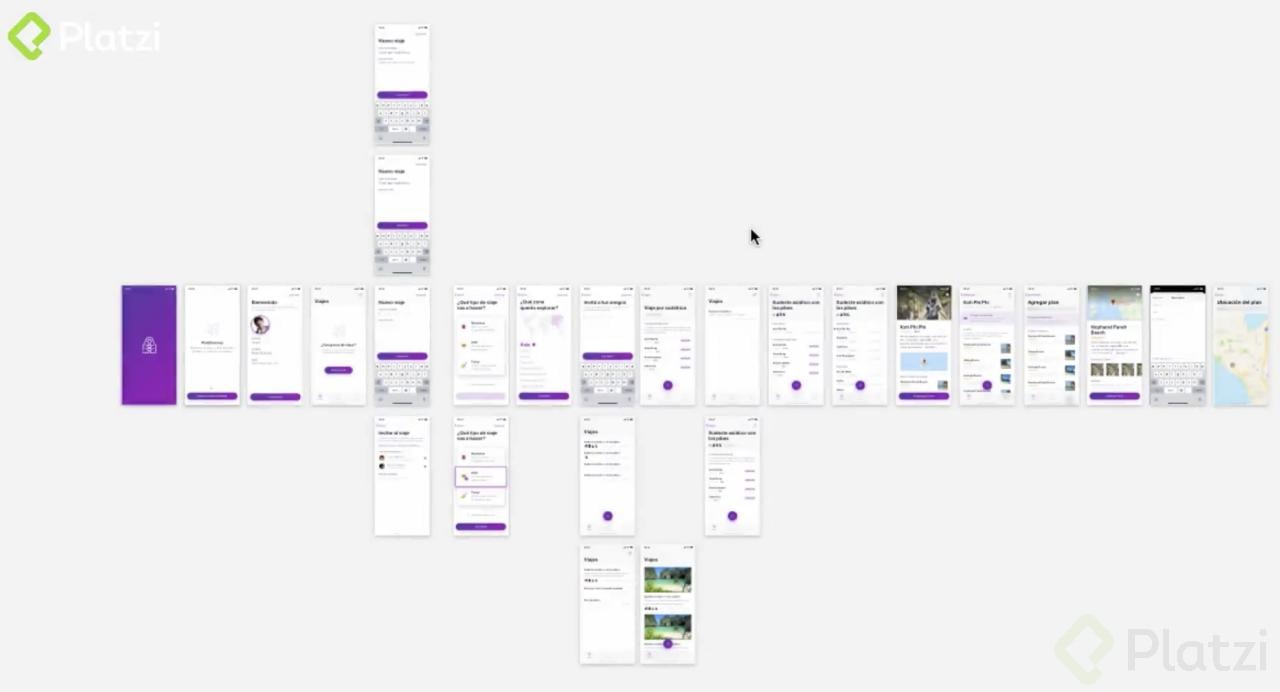
Sketch is the perfect application for designing digital interfaces. The entire professional design industry uses Sketch. AdobeXD is also available. Both are very cool. They allow us to create libraries with reusable components so that any changes in small components are instantly reflected on all screens.
It is also possible to design interfaces with Photoshop or Illustrator. And, although you can achieve the same results, it will be a bit more difficult. These tools are oriented towards illustration or bitmap editing. The best thing is to be open to all tools and new ways of working in this industry.
It is completely normal and professional to combine tools. For example, designing your logo in Illustrator, working with photos in Photoshop, and then composing everything at the end in Sketch.
Zeplin shows us the size, colors, and other properties of each element in our design. It even allows us to export the styles to Swift, Java, or CSS code. At Platzi, we live off Zeplin. There are also other similar tools like InVision Studio. But Zeplin is used in the industry.
1.3. Always think about User Experience and Usability
The interfaces of our applications are constantly evolving. The User Experience and Usability team is responsible for researching and conducting many tests and interviews to evaluate whether the application is actually solving the problems of users.
You might think that you don't have talent for design. But remember that the best applications in the world have design. And if you want to break through that barrier, you can learn the Fundamentals of Design. Then you can learn to Design Professional Interfaces.

2. Choose the programming tools to create mobile apps
Swift Playgrounds is an application for learning to program in a "fun" way, from Mac or iPad. You start by dragging and dropping. And gradually, it teaches you how to run small code experiments and how very small versions of an application work.
There is also App Inventor. A MIT platform that allows you to create your mobile applications by dragging and dropping elements. You choose what you want to run, and then you can export it.
However, we are the type of people who want to create professional applications, not just toys. For that, you need to actually program. And, of course, if you want to learn to program for creating professional apps, you can take the Free Basic Programming Course on Platzi.

3. Move on to professional mobile app development
3.1. Native Code
To start programming our app, we need to choose the operating system we will be working on: Android or iOS. We also need to decide which language we will be programming in.
Java is the language for writing native application code on Android. It is very strict, and its learning curve is very steep. However, for this reason, it helps us a lot to maintain applications when they become larger than normal.
Kotlin is an iteration of Java created by the Google team. It is a less strict language than Java, but not as relaxed as JavaScript. Remember that we still need to know Java to work with Kotlin.
To compile application code on Android, we use Android Studio. An IDE that works on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
Swift and Objective-C are the languages for writing native application code on IOS. Objective-C is a little faster. But the difference is almost not noticeable. Most apps are using Swift.
To compile application code on IOS, we use Xcode. An IDE that only works on Mac. That's it. We can only develop applications for IOS if we have a Mac.

3.2. Multiplatform Code
React Native is a bridge between native code and the application's frontend. It allows us to use JavaScript to create reactive components that we can use on both Android and IOS.
Using React Native does not mean that we should not rewrite code in Java/Kotlin or Swift/Objective-C. What really happens is that we can make very rapid progress on the codebase for both platforms. And then we will develop small parts of native code to develop special features (notifications, downloads…).
We must also remember that we still need Android Studio or XCode to compile our code.
Xamarin is a very similar tool. But it uses .Net instead of JavaScript. It has much more advanced options and plugins so that we do not need to write native code. But if, for some reason, we must use native code, it will take a very long time.
When companies become very large and have a lot of money, they can have a specialized team for each platform. But most companies do not have the capacity to invest in such teams and maintain the development of both products in parallel. In that case, tools like React Native are a very good option. 👉 How Airbnb develops native apps now that Airbnb-React is Vintage
Flutter is a technology for designing and developing native interfaces on iOS and Android using Dart. It also allows us to work with web or desktop applications. It is a tool that is definitely worth learning.
3.3. Databases, Backend and APIs
Surely you're wondering, what are databases? Well, they're the place where we store and query the data for our application. There are many databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB.
But how do you choose the best database for your application?
It depends. There are relational databases, document databases, graph databases, and more. There is a database that can give you the best solution for each problem.
👉 What is SQL and NoSQL?
Backend Languages are responsible for communicating with the database, retrieving the information, and delivering it to the mobile application. You can use Python with Django, Ruby on Rails, Node.js, PHP with Laravel, Java, .NET, or any other language.
The important thing is that the frontend code of the application does not communicate directly with the database. That would be a very serious security error. Always treat Java and Kotlin or Swift and Objective-c as if they were HTML and JavaScript.
APIs are predictable data structures that are responsible for communicating between the backend and the frontend, and data and what users see.
In the past, we used SOAP and XML. But modern APIs use REST. Services work with JSON. It looks like JavaScript code. But in reality, they are encapsulated data that the application can then capture as normal variables.
But we also have GraphQL. The most modern and popular data transport layer. It's almost like a scripting language. It handles everything. It makes it easier for the frontend to access the different data we need without the backend having to do more work.
3.4. Firebase
Firebase is one of the few "all-in-one" systems. It handles the database, backend, and data transport with APIs. The disadvantage is that we don't have complete control over the database or the scalability of our services. And, in addition, we have to pay.
Many famous applications (Tinder) have used Firebase to start their prototype. And, eventually, when they grow, they integrate database, backend, and data transport teams. You can follow the same path.
Conclusions
Now that you have a better understanding of how to make a mobile app, it's time to start creating your own. You have different platforms to do so, you just need to believe in yourself. In the next video, Freddy Vega explains how to create your first app on Android and iOS.
This is the mobile app development universe in 2021. Now that you know, what app will you build? What tools will you use?
Interface Design, Basic Programming, Mobile Development, and Backend Development.
The development of mobile applications is one of the most challenging areas in creating technology products. But it is also one of the most exciting. Remember that the entire world today is mobile-first. And Platzi accompanies you in this entire process from scratch.
#NeverStopLearning